- KNOWLEDGE BASE
- EATING DISORDERS
- General Topics
- No posts found for the specified taxonomy and term.
- General Topics
- EATING DISORDERS

SWISS MEDICAL EXPERTISE: ZURICH, MALLORCA, LONDON, MARBELLA


CONDITIONS WE TREAT
PROGRAMS
Intensive residential treatment program starting from 4 weeks. Location: Mallorca, Zurich, London.
Comprehensive second opinion assessments for both psychiatric and general health concerns. Location: Mallorca, Zurich, London
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION




10 Minutes
CONTENTS
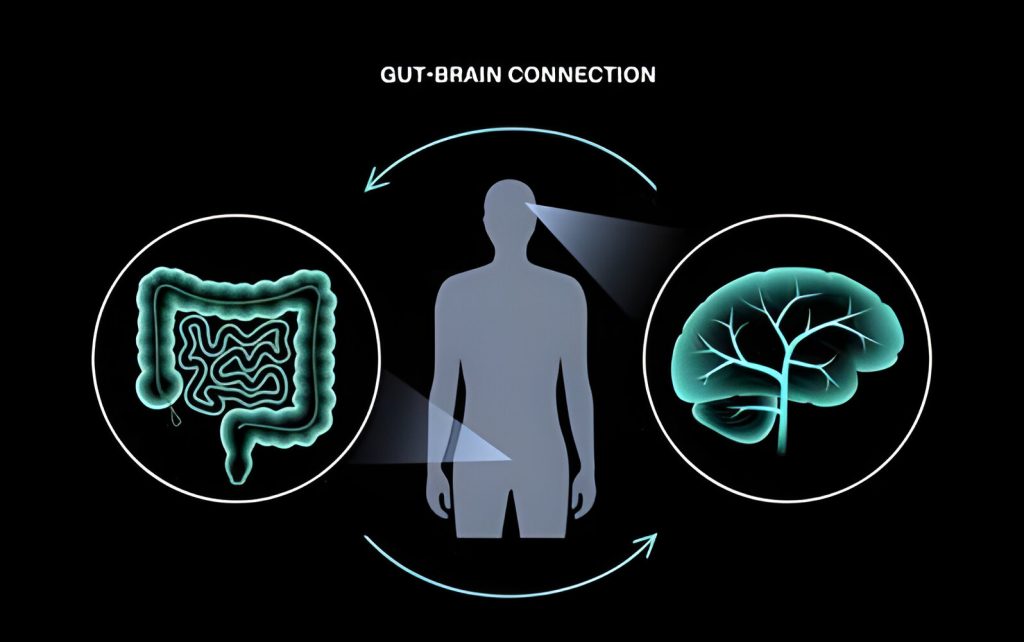
With evolving research, the scientific community has unraveled a close connection between the digestive system and mental health. This unique connection, especially in terms of gut health and anxiety, has garnered massive attention, over the past few years. Often referred to as the gut-brain axis, this intricate relationship highlights how the digestive system can directly influence your mental well-being. [1]
To understand this link and use it to benefit the gut and mental health, it is essential to understand it both individually and as a single unit that works bi-directionally.
Also known as the gastrointestinal tract, the gut is a complex system in the human body responsible for breaking down and processing food. The system begins from the mouth and ends at the anus, while surpassing many essential organs in the way, such as the stomach, intestines, and colon. Some crucial gut functions include nutrient absorption and processing, digestion, and waste elimination. However, more recent research has confirmed its role in many other processes, such as regulating mental health.
Read Also About Anxiety And Diarrhea
Hidden within the gut is an extensive network comprising millions of neurons, which is known as the enteric nervous system. [2] This network closely communicates with the brain through hormonal, neural, and immune system pathways, forming the gut-brain axis. This axis has a bi-directional relationship, meaning both the central nervous system and the enteric nervous system influence each other’s function.
Apart from the enteric nervous system, the gut shelters a community of microorganisms, including viruses, bacteria, and fungi. These populations comprising trillions of these organisms collectively form the microbiome and play an active role in regulating various body functions. For instance, these microorganisms support digestive processes, regulate the immune system, and produce essential vitamins. More importantly, the gut microbiome also synthesizes neurotransmitters, such as dopamine, serotonin, and gaba-aminobutyric acid (GABA) which impact the nervous system and regulate the mood. [3]
It is common for everyone to experience some form of anxiety from time to time. However, when the issue becomes more persistent and severe and prevents a person from living their daily life, it is known as anxiety disorder. Experts describe anxiety disorders as a group of conditions closely connected that cause persistent worry or fear in situations that do not seem threatening.
Some common symptoms of an anxiety disorder include the following:
As mentioned above, the gut-brain axis is a powerful communication network in the human body that closely links the cognitive and emotional centers in the brain with the intestinal functions. Multiple pathways control this axis, such as the hormonal, immune, and nervous systems.
Mentioned below are the proposed theories that relate anxiety and the gut:
Research confirms a strong correlation between gut health and anxiety through the following mechanisms:
Dysbiosis defines any imbalance in the gut microbiome. This imbalance is often strong enough to disrupt the natural production of neurotransmitters by these bacterial colonies, leading to mood dysregulation. Studies have found that many anxious individuals have imbalances in their microbiomes, further confirming the link between gut bacteria and anxiety.
Chronic inflammation is a key factor affecting the brain’s functions. Any inflammatory gut disease releases pro-inflammatory markers that cross the blood-brain barrier to affect brain areas directly involved in mood regulation, such as the amygdala and hippocampus. This dysregulation can set the stage for anxiety disorders.
Having a healthy population of gut bacteria ensures optimal stress response. Conversely, an unhealthy gut can exacerbate the natural stress response, pushing an individual into a hypervigilant state. When this goes on for a long time, it can lead to anxiety disorders.
Leaky gut syndrome is a disorder that increases intestinal permeability, allowing toxins and undigested food to enter the bloodstream. This hyperpermeability causes system-wide inflammation and triggers the immune system to respond to these toxins. With time, the persistently high inflammation levels cause anxiety and other mood disorders. [5]
Diet plays a significant role in maintaining gut health and mental well-being. Many food items promote healthy gut bacteria while others can cause imbalances. Following are the foods to eat and avoid to ensure a healthy balance:
In addition to dietary modification, other aspects of everyday life also impact the gut health and anxiety levels. These factors include the following:
Prebiotics and probiotics have gained popularity for their potential to positively influence gut health. Probiotics include live bacteria that improve the gut microbiome whereas prebiotics include non-digestible fibers that serve as food for them. Psychobiotics is a new term that provides the body with a combination of prebiotics and probiotics to improve mental health. [6]
Where lifestyle changes and dietary modifications are not successful in managing gut health issues and anxiety, it becomes essential to get professional assistance. Various healthcare providers, such as dieticians, doctors, and mental health professionals, can provide personalized advice and plan of care according to individual circumstances.
The following are the components of a professional treatment program for gut health and anxiety:
With the sharp rise in the global burden of gut issues and mental health disorders, experts are dedicated to uncovering new treatment plans to manage both together. At present, the following prospects are being looked into:
The intricate relationship between gut health and anxiety indicates a complex interplay between mental and physical well-being. Understanding how the gut-brain axis works and the connection between gut bacteria and anxiety provide valuable insights into how to support overall health.
The best way to manage both gut health issues and anxiety is through an integrative approach that combines stress management, a healthy diet, and exercise. Professional guidance must be sought as needed to nurture the gut and mind. Ongoing research exploring these domains brings hope for new and improved approaches for a better quality of life for individuals with gut health issues and anxiety.
[5] Maes M. The cytokine hypothesis of depression: inflammation, oxidative & nitrosative stress (IO&NS) and leaky gut as new targets for adjunctive treatments in depression. Neuroendocrinology letters. 2008 Jun 1;29(3):287-91.
There are different ways in which gut health can cause anxiety. Any imbalances in the gut microbiome disrupt the production of mood-regulating neurotransmitters, leading to anxiety. An unhealthy gut is also known to trigger the body’s stress response, contributing to anxiety. Lastly, certain pro-inflammatory gut issues, such as IBS and leaky gut, also interrupt mood regulation, making you more anxious.
Following are the signs to look out for if you believe you have poor gut health:
Food intolerances
Digestive issues, such as diarrhea, constipation, gas, and bloating
Skin problems like acne and eczema
Mood disorders, such as depression and anxiety
Chronic fatigue
Frequent illnesses or infections
Antibiotics can imbalance the beneficial bacteria in the gut by possibly killing some of them. This disruption triggers dysbiosis that causes inflammation and dysregulates the production of mood-regulating hormones, consequently heightening anxiety levels. Taking probiotics to restore the gut microbiome is imperative to keep things in control.
Consider getting professional help if you have:
Persistent, severe anxiety that continues to interfere with your daily life
Symptoms of an underlying gut issue, such as celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and IBS
Chronic digestive problems unresponsive to lifestyle management
COGNIFUL is a leading provider of luxury addiction and mental health treatment for affluent individuals and their families, offering a blend of innovative science and holistic methods with unparalleled individualised care.
We believe in the healing power of a community that brings together collective wisdom and individual insight from collective group sessions and activities. We offer a variety of activities and therapies, from group workshops to communal living experiences, every aspect of our program is designed to foster growth, understanding, and self-improvement.
more infoOur program is uniquely designed to meet your needs, with our team closely monitoring your progress. Our therapists are committed to addressing the underlying causes of your challenges, not just the surface symptoms. This deep, root-level therapy extends beyond your stay with us, ensuring enduring success and well-being.
more infoOur team of specialists integrates the most effective strategies from psychological care and holistic medicine, offering you personalized support. This approach includes a range of complementary therapies, all seamlessly coordinated to work together in a comprehensive, integrative manner for your benefit.
more infoThroughout your stay, our dedicated team will ensure a personalized and nurturing experience, providing continuous support and attention. We are committed to guiding you through every step of this transformative journey.
more infoNestled in a serene location close to the calming embrace of the beach, our luxury residence is designed with healing in mind, featuring private suites that offer an oasis of tranquility. Each suite is crafted to provide a personal sanctuary where individuals can reflect, rejuvenate, and recover in peace.
more infoComplex trauma frequently underlies both mental and physical distress. We offer a secure environment, incorporating integrated trauma treatment techniques to facilitate the healing process.
more info