- KNOWLEDGE BASE
- EATING DISORDERS
- General Topics
- No posts found for the specified taxonomy and term.
- General Topics
- EATING DISORDERS

SWISS MEDICAL EXPERTISE: ZURICH, MALLORCA, LONDON, MARBELLA


CONDITIONS WE TREAT
PROGRAMS
Intensive residential treatment program starting from 4 weeks. Location: Mallorca, Zurich, London.
Comprehensive second opinion assessments for both psychiatric and general health concerns. Location: Mallorca, Zurich, London
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION




11 Minutes
CONTENTS
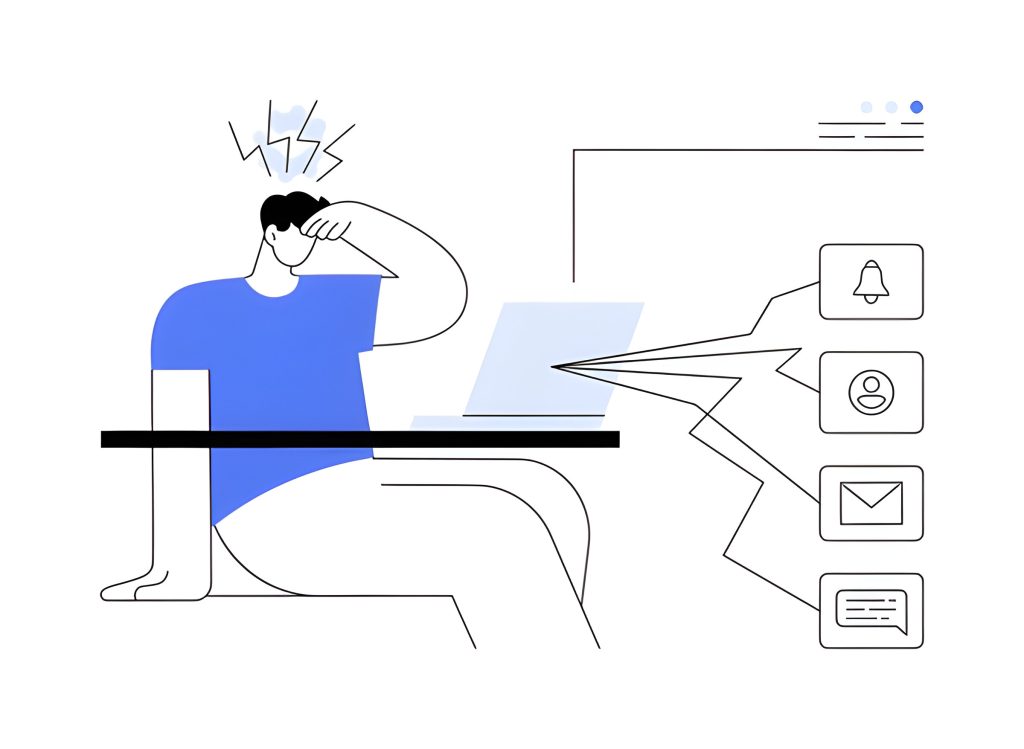
With rapid technological advancements and heavy digitalization, global mental health has taken a significant toll. Problems like hyperstimulation anxiety slowly emerged as a part of the digitally connected, fast-paced world of today and quickly rose to become a significant concern. Also known as sensory overload, hyperstimulation anxiety is a state of mind where a person’s nervous system becomes overwhelmed due to excessive stimuli, leading to high anxiety and stress levels. [1]
Hyperstimulation anxiety is becoming progressively prevalent, particularly due to increasing exposure to social pressures, different forms of media, and the growing demands of modern life. Understanding hyperstimulation anxiety and its mechanisms and management is crucial to minimizing its negative effects on life.
Hyperstimulation anxiety occurs when a person is exposed to a high amount of sensory input enough to overwhelm them. Some examples of this sensory input include visual stimuli, noise, and information. This overstimulation can exhaust the brain’s ability to process, leading to stress, anxiety, and discomfort.
The following are the potential causes that can lead to hyperstimulation anxiety:
Hyperstimulation anxiety has various neurological mechanisms involved according to the research so far. The human brain comprises a complex network of neurotransmitters and neurons that shape the responses to stimuli. Due to exposure to excessive sensory input, certain areas of the brain, including the amygdala, can become overactive, leading to a hyper-stimulated state that perpetuates anxiety. [2]
Following are the neural mechanisms that may trigger hyperstimulation anxiety in a person:
The following psychological and behavioral aspects can affect the risk of acquiring hyperstimulation anxiety:
In addition to behavioral, psychological, and neural causes, many societal and cultural influences can contribute to hyperstimulation anxiety. These factors may include the following:
Hyperstimulation anxiety can affect various aspects of everyday life with widespread effects. Some of these include the following:
There are multiple ways to keep hyperstimulation anxiety in control. Some of them include the following:
Anti-inflammatory foods are essential for the regulation of brain health and the management of anxiety. [7] These food items provide the body with antioxidants that protect the brain from oxidative stress while calming the nervous system.
Following are some foods to include in your daily diet for managing hyperstimulation anxiety:
These foods can stabilize blood sugar and avoid sudden spikes and dips, leading to anxiety reduction. Whole grains like oats and quinoa, brown rice, and legumes, including lentils and beans, can also provide fiber and vitamin B complex that ensure a steady release of energy. Moreover, they prevent blood sugar crashes that can contribute to hyperstimulation anxiety.
Magnesium is an important nutrient that regulates neurotransmitters and promotes a calmer nervous system. Some good examples of magnesium-rich foods include spinach, kale, pumpkin seeds, almonds, and whole grains. Including these foods in a daily diet can alleviate the symptoms of anxiety.
B vitamins are crucial to maintain brain health. These vitamins are naturally available in leafy green vegetables, whole grains, and meat products including turkey and chicken. Additionally, Brussels sprouts, blueberries, dark chocolate, and broccoli can also protect the brain from the side effects of oxidative stress.
The gut microbiome is known to have a direct relationship with mental health. Supplementing this microbiome with foods like kefir, kimchi, sauerkraut, and yogurts with live cultures can promote gut health and consequently benefit mental health. [8]
Herbal teas, including lavender and chamomile, can relax the brain which consequently helps keep hyperstimulation anxiety in control. Maintaining adequate hydration levels is also necessary. Aim to drink 6 to 8 glasses of water in addition to herbal teas to support mental health.
Society, culture, and community play integral roles when it comes to managing hyperstimulation anxiety.
Healthcare providers play a critical role in the diagnosis and management of hyperstimulation anxiety. They can extend support through different interventions, such as the following:
Hyperstimulation anxiety is a complex condition that requires a multifaceted approach for effective management. Exploring its potential neurobiological mechanisms and adopting tailored coping strategies in a community-based holistic environment can help keep the associated challenges under control. While many hyperstimulation anxiety treatment modalities are available at present, more research and community support are required to help such people thrive among the general complexities of life. Through collective effect and innovative approaches, it is possible to pave the way for a brighter future with the mitigation of hyperstimulation anxiety.
1 Carpenter KLH, Baranek GT, Copeland WE, Compton S, Zucker N, Dawson G, Egger HL. Sensory Over-Responsivity: An Early Risk Factor for Anxiety and Behavioral Challenges in Young Children. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2019 Jun;47(6):1075-1088. doi: 10.1007/s10802-018-0502-y. PMID: 30569253; PMCID: PMC6508996.
2 Carpenter KLH, Baranek GT, Copeland WE, Compton S, Zucker N, Dawson G, Egger HL. Sensory Over-Responsivity: An Early Risk Factor for Anxiety and Behavioral Challenges in Young Children. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2019 Jun;47(6):1075-1088. doi: 10.1007/s10802-018-0502-y. PMID: 30569253; PMCID: PMC6508996.
3 Huang SH, Liu WZ, Qin X, Guo CY, Xiong QC, Wang Y, Hu P, Pan BX, Zhang WH. Association of Increased Amygdala Activity with Stress-Induced Anxiety but not Social Avoidance Behavior in Mice. Neurosci Bull. 2022 Jan;38(1):16-28. doi: 10.1007/s12264-021-00762-0. Epub 2021 Sep 7. PMID: 34494228; PMCID: PMC8782949.
4 Kenwood MM, Kalin NH, Barbas H. The prefrontal cortex, pathological anxiety, and anxiety disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2022 Jan;47(1):260-275. doi: 10.1038/s41386-021-01109-z. Epub 2021 Aug 16. Erratum in: Neuropsychopharmacology. 2022 Apr;47(5):1141. doi: 10.1038/s41386-021-01216-x. PMID: 34400783; PMCID: PMC8617307.
While the general symptoms vary, some of them include the following:
Feeling frazzled or overwhelmed
Exhaustion and fatigue
Poor concentration
Palpitations/ increased heart rate
Sleep disturbances, such as restless sleep or insomnia
Mood swings
Irritability
Hyperstimulation anxiety tingling and numbness is also a commonly reported symptom in many individuals.
There is no set duration of recovery when it comes to hyperstimulation anxiety. Some people may continue to experience it for months while others may notice improvements within a few weeks of starting treatment.
If unmanaged, hyperstimulation anxiety can lead to many chronic mental health issues, such as depression and generalized anxiety disorder. Additionally, it predisposes a person to various physical health issues, such as chronic pain and cardiovascular problems. Some other long-term effects include a poorer quality of life due to negative impacts on work, relationships, and overall well-being.
COGNIFUL is a leading provider of luxury addiction and mental health treatment for affluent individuals and their families, offering a blend of innovative science and holistic methods with unparalleled individualised care.
We believe in the healing power of a community that brings together collective wisdom and individual insight from collective group sessions and activities. We offer a variety of activities and therapies, from group workshops to communal living experiences, every aspect of our program is designed to foster growth, understanding, and self-improvement.
more infoOur program is uniquely designed to meet your needs, with our team closely monitoring your progress. Our therapists are committed to addressing the underlying causes of your challenges, not just the surface symptoms. This deep, root-level therapy extends beyond your stay with us, ensuring enduring success and well-being.
more infoOur team of specialists integrates the most effective strategies from psychological care and holistic medicine, offering you personalized support. This approach includes a range of complementary therapies, all seamlessly coordinated to work together in a comprehensive, integrative manner for your benefit.
more infoThroughout your stay, our dedicated team will ensure a personalized and nurturing experience, providing continuous support and attention. We are committed to guiding you through every step of this transformative journey.
more infoNestled in a serene location close to the calming embrace of the beach, our luxury residence is designed with healing in mind, featuring private suites that offer an oasis of tranquility. Each suite is crafted to provide a personal sanctuary where individuals can reflect, rejuvenate, and recover in peace.
more infoComplex trauma frequently underlies both mental and physical distress. We offer a secure environment, incorporating integrated trauma treatment techniques to facilitate the healing process.
more info